Discover EBIT and EBITDA, critical financial metrics that reveal a company’s operational performance and cash flow. Understand their significance and application in financial analysis – suitable for students and economics enthusiasts alike.
Introduction
In the world of finance, understanding the nuances of financial metrics is essential for investors, analysts, and business owners. Two commonly used measures that play a crucial role in financial analysis are EBIT (Earnings Before Interest and Taxes) and EBITDA (Earnings Before Interest, Taxes, Depreciation, and Amortization). In this article, we’ll delve into the meaning of EBIT and EBITDA, their significance, and how they work to provide valuable insights into a company’s financial health.
What is EBIT and EBITDA?

1. EBIT (Earnings Before Interest and Taxes):
EBIT, also known as operating income or operating profit, is a measure of a company’s profitability before accounting for interest expenses and income taxes. It represents the core operating performance of a business, making it a valuable metric for assessing the company’s operational efficiency.
2. EBITDA (Earnings Before Interest, Taxes, Depreciation, and Amortization):
EBITDA is a more comprehensive measure of a company’s financial performance. It adds back not only interest and taxes but also depreciation and amortization expenses to EBIT. EBITDA provides a clearer picture of a company’s overall ability to generate cash from its operations, as it excludes non-cash expenses like depreciation and amortization.
How EBIT and EBITDA Work
1. EBIT (Earnings Before Interest and Taxes):
- Start with Revenue: Begin with a company’s total revenue, representing the income generated from its primary operations.
- Subtract Operating Expenses: Deduct the cost of goods sold (COGS), operating expenses, and other operating costs from the revenue. This step gives you the EBIT.
Formula: EBIT = Revenue – COGS – Operating Expenses
2. EBITDA (Earnings Before Interest, Taxes, Depreciation, and Amortization):
- Begin with EBIT: Start with the EBIT, which has already accounted for revenue and operating expenses.
- Add Back Depreciation and Amortization: To calculate EBITDA, you need to add back depreciation and amortization expenses, which are non-cash items. This provides a clearer picture of a company’s cash flow from its operations.
Formula: EBITDA = EBIT + Depreciation + Amortization
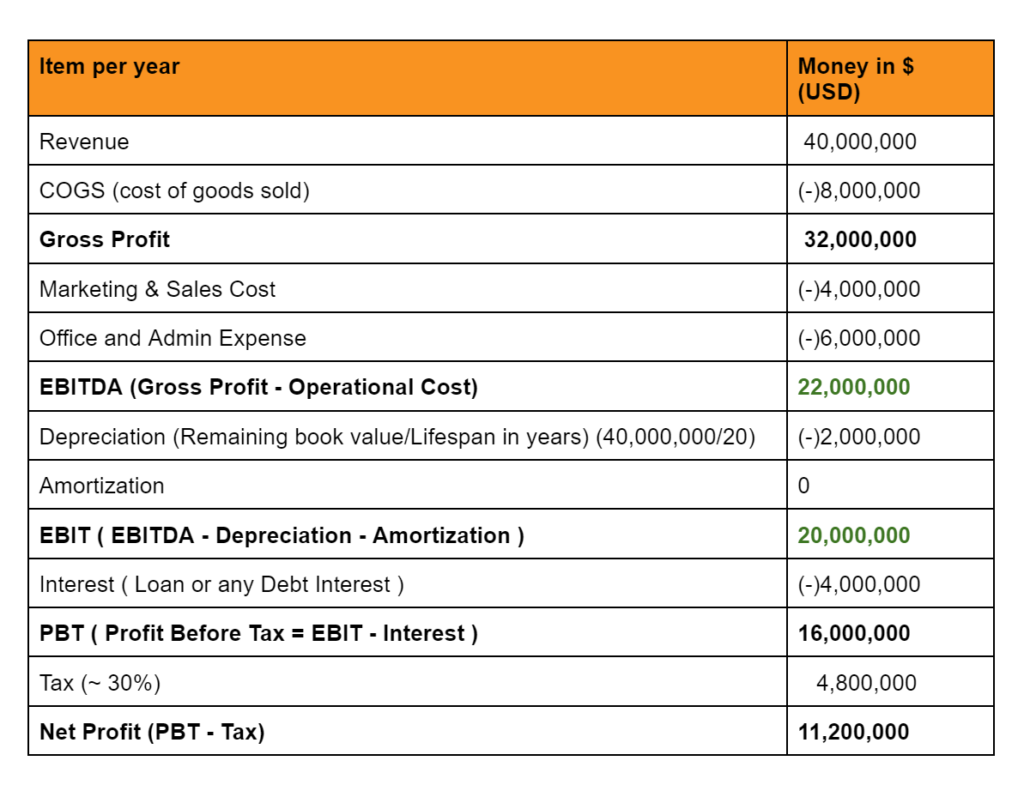
Certainly, let’s illustrate the calculation of EBIT and EBITDA using a hypothetical example. Imagine a small tech company, XYZ Inc., with the following financial data for the fiscal year 20XX:
- Total Revenue: $1,000,000
- Cost of Goods Sold (COGS): $400,000
- Operating Expenses: $250,000
- Depreciation Expense: $50,000
- Amortization Expense: $20,000
- Interest Expense: $30,000
- Income Tax Expense: $40,000
We’ll start by calculating EBIT (Earnings Before Interest and Taxes) for XYZ Inc.:
EBIT = Total Revenue – COGS – Operating Expenses
EBIT = $1,000,000 – $400,000 – $250,000 = $350,000
So, XYZ Inc.’s EBIT for the fiscal year 20XX is $350,000.
Now, let’s calculate EBITDA (Earnings Before Interest, Taxes, Depreciation, and Amortization) for the same company:
EBITDA = EBIT + Depreciation + Amortization
EBITDA = $350,000 + $50,000 + $20,000 = $420,000
XYZ Inc.’s EBITDA for the fiscal year 20XX is $420,000.
Now, let’s understand the significance of these values:
- EBIT ($350,000): This figure represents XYZ Inc.’s operating profit before considering interest expenses and income tax. It shows how well the company performed in terms of generating income from its core operations.
- EBITDA ($420,000): EBITDA is a more comprehensive measure, as it adds back not only interest and taxes but also depreciation and amortization expenses. In this case, it reveals that the company generated $420,000 from its operations, excluding non-cash expenses like depreciation and amortization. This metric is crucial for assessing the company’s cash flow-generating capacity.
In this example, understanding EBIT and EBITDA helps investors and analysts evaluate XYZ Inc.’s financial performance and assess its ability to generate cash from its operations. It also facilitates comparisons with other companies in the industry, allowing for better-informed investment decisions and financial analysis.
Know the basic terms of technical analysis of stock market: Understanding Top Line, Bottom Line, Bid Price, Offer Price, and Volume in Stock Market
Know about the various trends and openings of stock market and how they affect Indian markets: Mastering Stock Market Fundamentals: Bearish and Bullish Trends, Gap-Up/Gap-Down Openings, and More
Significance of EBIT and EBITDA:
- Operational Performance: EBIT and EBITDA are excellent indicators of a company’s core operational performance, helping investors assess how well a company is performing before considering financial costs or non-cash expenses.
- Comparability: These metrics facilitate comparisons between companies in the same industry or sector, as they strip away differences in financing and accounting choices.
- Cash Flow Assessment: EBITDA, in particular, is valuable for evaluating a company’s cash generation capacity, as it excludes non-cash expenses like depreciation and amortization.
- Investment Decisions: EBIT and EBITDA are essential in financial modeling, valuation, and investment decisions. They play a critical role in assessing a company’s ability to service debt, make capital investments, and generate returns for shareholders.
- Acquisition and Mergers: These metrics are often used to determine the value of a target company, making them vital in acquisition and merger transactions.
Conclusion
EBIT and EBITDA are key financial metrics used in financial analysis to assess a company’s operational performance and cash flow-generating capacity. Understanding how to calculate EBIT and EBITDA and their significance is crucial for making informed investment decisions, conducting business valuations, and comparing companies within the same industry. These metrics provide a clearer and more standardized view of a company’s financial health, allowing investors and analysts to make more informed decisions.
Know, what are Indian stock market indices: Understanding India’s Stock Market Indices: Nifty 50, Nifty Bank, Nifty Sensex, and More
Also know, what are Global market indices: Understanding FIIs, DIIs, HNIs, RIIs, Depositories, and Global Indices Influencing the Indian Stock Market
Analyse EBITDA of any stock at https://www.chittorgarh.com/ OR at https://www.moneycontrol.com/
FAQs
What is EBIT and EBITDA?
Answer: EBIT stands for Earnings Before Interest and Taxes, while EBITDA stands for Earnings Before Interest, Taxes, Depreciation, and Amortization. These are financial metrics used to assess a company’s operating performance and cash flow generation.
2. Why are EBIT and EBITDA important for investors?
Answer: EBIT and EBITDA are important for investors because they provide insights into a company’s core operational profitability and cash flow, allowing for better investment decisions, industry comparisons, and financial analysis.
3. What are the key differences between EBIT and EBITDA?
Answer: The main difference is that EBIT includes interest and taxes, while EBITDA adds back depreciation and amortization expenses. EBIT measures profitability before interest and taxes, and EBITDA provides a more comprehensive view of cash flow generation by excluding non-cash expenses.