Discover the world of stock trading with our comprehensive guide on various types of stock orders, including Limit, Market, Stop Loss, After Market, IOC, and GTC orders. Learn how to make informed decisions and optimize your trading strategy. Explore now!
Introduction

When it comes to trading stocks in the financial markets, understanding the different types of stock orders is crucial. These orders serve as the instructions you provide to your broker, dictating how and when you want to buy or sell a particular security. In this article, we will delve into the various types of stock orders, including Limit Orders, Market Price Orders, Stop Loss Orders, After Market Orders, Immediate or Cancel (IOC) Orders, and Good ‘Till Day (GTC) Orders.
TYPES OF STOCK ORDERS:
Limit Orders
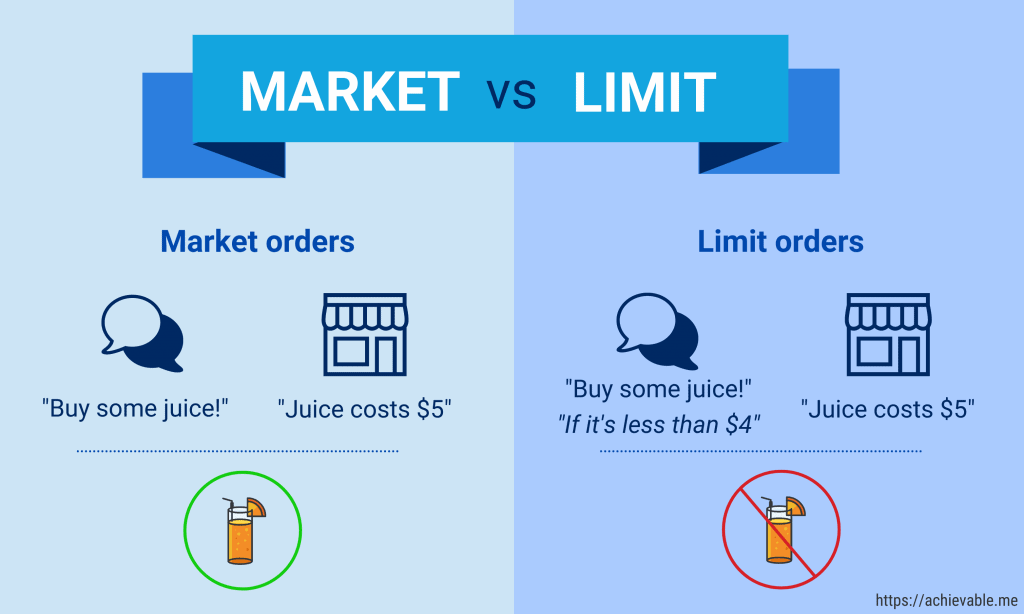
A Limit Order is a popular order type among traders. It allows you to specify the price at which you want to buy or sell a stock. If the stock’s market price reaches the limit price you set, the order will be executed. However, there’s no guarantee that the order will be filled if the market price doesn’t reach your specified limit.
Market Price Orders
Market Price Orders are the simplest form of stock orders. When you place a Market Price Order, you are instructing your broker to buy or sell a stock at the current market price. This type of order is executed immediately since it doesn’t have a price constraint.
Stop Loss Orders

Stop Loss Orders are used to limit potential losses. When you set a Stop Loss Order, you specify a price level at which you want to sell a stock if its price starts to fall. This order can help protect your investment by automatically selling the stock when the price reaches the predefined stop loss level.
Know the key terms of technical analysis of stocks: Understanding Top Line, Bottom Line, Bid Price, Offer Price, and Volume in Stock Market
Types of trends and market openings to know before investing: Mastering Stock Market Fundamentals: Bearish and Bullish Trends, Gap-Up/Gap-Down Openings, and More
After Market Orders
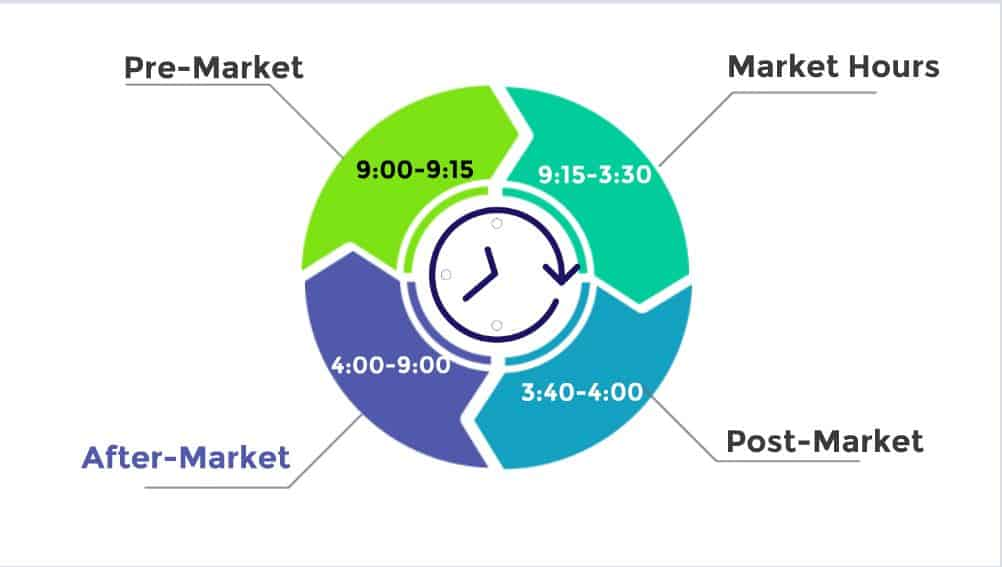
After Market Orders, also known as After-Hours Orders, allow you to place orders outside of regular trading hours. Stock markets have set trading hours, but news and events can impact stock prices even when the market is closed. After Market Orders enable you to react to such developments by placing orders during extended trading hours.
Immediate or Cancel (IOC) Orders

Immediate or Cancel Orders are designed for traders who want their orders executed immediately or not at all. If an IOC Order can’t be filled entirely, the unfilled portion is canceled. This type of order is often used when traders want to capture a specific market price quickly
Good ‘Till Day (GTC) Orders

Good ‘Till Day Orders are perfect for long-term investors or those with specific trading strategies. When you place a GTC Order, it remains active until it’s executed, canceled, or for a specified number of days, usually up to 90 days. This allows you to set and forget your order, knowing that it will be active until your criteria are met.
How to analyse markets? What is Support and Resistance?
Place your stock order at https://www.moneycontrol.com/
Conclusion
Understanding the different types of stock orders is essential for successful trading. Each order type serves a specific purpose and caters to various trading strategies. Whether you’re a day trader, a long-term investor, or somewhere in between, knowing when and how to use Limit Orders, Market Price Orders, Stop Loss Orders, After Market Orders, IOC Orders, and GTC Orders can help you navigate the complex world of stock trading with confidence. Make sure to consult with your broker or financial advisor to determine the most suitable order types for your trading needs and risk tolerance.
FAQs
- What is the main difference between a Limit Order and a Market Price Order?
- Answer: The key distinction between these two order types lies in pricing. A Limit Order allows you to specify a particular price at which you want to buy or sell a stock. In contrast, a Market Price Order instructs your broker to execute the trade at the current market price, without any price constraints.
- How can Stop Loss Orders help me manage risk in my stock investments?
- Answer: Stop Loss Orders are a risk management tool. When you set a stop loss price, it acts as an automatic trigger to sell a stock if its price drops to or below that level. This helps protect your investment by limiting potential losses and ensures you don’t have to constantly monitor the market.
- What are the benefits of using Good ‘Till Day (GTC) Orders in my trading strategy?
- Answer: Good ‘Till Day Orders are ideal for traders with long-term or specific trading strategies. They remain active until executed, canceled, or until a specified number of days, often up to 90 days. This provides flexibility and convenience, allowing you to set your order and have it active until your predefined criteria are met, without having to place the order repeatedly.